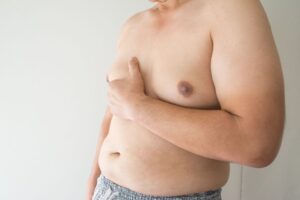
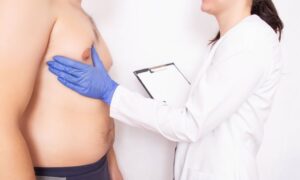
Gynecomastia is a common condition in men that causes excess breast tissue development, often leading to discomfort and self-consciousness. If you’ve noticed swelling, a firm lump beneath your nipple, or tenderness in your chest, you may be wondering if that might be gynecomastia. The way to tell is to look for a rubbery or firm mass directly under the nipple, often accompanied by breast tenderness or a subtle change in contour, which is distinct from soft, evenly distributed chest fat. A thorough self-exam and a consultation with a qualified plastic surgeon like Dr. Erella at Aspira Plastic Surgery can confirm the diagnosis and guide you toward treatment options.
—
Facts About Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia refers to the benign enlargement of breast glandular tissue in men. It is not simply a buildup of fat, but an actual increase in the gland tissue beneath the nipple and areola, sometimes accompanied by excess fatty tissue. This condition can affect one or both breasts and may appear at any age.
- Gynecomastia affects up to 70% of adolescent boys at some point and is also common in adult men.
- It can be temporary, related to puberty or hormone changes, or may persist into adulthood.
- While not physically harmful, gynecomastia can impact confidence and quality of life.
—
Signs and Symptoms
Gynecomastia usually presents as a firm, rubbery mound of tissue directly beneath the nipple-areolar complex. This tissue is more localized and distinct than general chest fat, often resulting in a puffy nipple or a more feminine chest contour.
Common symptoms include:
- Swelling or fullness beneath the nipple
- Firm, disc-like tissue (not just soft fat)
- Puffiness or protruding nipples
- Breast tenderness or sensitivity
- Asymmetry (one breast larger than the other)
Gynecomastia can be mildly tender, especially during early stages or periods of rapid growth. Some men experience sensitivity or achiness, but severe pain is uncommon. This condition commonly occurs during puberty, due to aging, or as a result of certain medical conditions.
—
What Causes Gynecomastia?
Medications
Anti-Androgens (Used in Prostate Treatment)
Anti-androgens, which are commonly used in prostate treatment, can cause enlarged male breast tissue by blocking the effects of testosterone. This hormonal shift gives estrogen a stronger influence on breast tissue growth. As a result, men taking these medications may notice swelling or firmness in the chest area.
Certain Antidepressants
Certain antidepressants have been associated with gynecomastia because they can affect hormone levels or the way hormones interact in the body. Although the exact mechanism isn’t always clear, these medications may increase estrogen activity or disrupt the balance between estrogen and testosterone. This hormonal imbalance can lead to the development of breast tissue in men.
Anabolic Steroids
Anabolic steroids significantly impact testosterone levels, often causing an imbalance that favors estrogen’s effects. This shift encourages breast tissue growth, sometimes resulting in visible enlargement and tenderness. Men using these substances for bodybuilding or athletic performance are particularly at risk.
Some Heart Medications
Some heart medications, such as calcium channel blockers and antiarrhythmic drugs, may cause gynecomastia by interfering with hormone metabolism or causing fluid retention. These side effects can lead to swelling and increased breast tissue. While not common, this cause should be considered when breast enlargement occurs during heart treatment.
Alcohol, Marijuana, and Certain Illicit Drugs
Alcohol, marijuana, and certain illicit drugs can all contribute to hormonal imbalances that promote the formation of excess tissue in the chest. Chronic use of these substances may increase estrogen levels or disrupt normal testosterone production. This leads to noticeable breast enlargement in some men.
Underlying Health Conditions
Liver or Kidney Disease
Liver or kidney disease can cause hormone processing problems, resulting in elevated estrogen levels that stimulate breast tissue growth. These conditions reduce the body’s ability to break down hormones properly, causing them to accumulate. As a result, men with liver or kidney disease often develop gynecomastia.
Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders, especially hyperthyroidism, increase hormone levels that can promote breast gland growth. Excess thyroid hormones accelerate metabolism and can disrupt the estrogen-testosterone balance. This often leads to the development of gynecomastia in affected men.
Tumors That Affect Hormone Production
Tumors that affect hormone production, such as those in the testes, adrenal glands, or pituitary gland, can cause abnormal increases in hormones that stimulate the breast glands. This hormone imbalance results in the growth of glandular breast tissue and breast enlargement. Detecting and treating these tumors is critical to managing gynecomastia caused by this factor.
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer in men is rare but must be distinguished from gynecomastia because it involves malignant growth of glandular breast tissue. Unlike benign gynecomastia, cancer usually presents as a hard, irregular lump and may be accompanied by skin changes or nipple discharge. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for the best outcomes.
Other Causes Leading to Hormone Changes
Certain herbal supplements (such as tea tree oil or lavender) have weak estrogenic effects and may contribute to this condition. Over-the-counter supplements or bodybuilding products sometimes play a role. Gynecomastia produces a firm, localized mass directly behind the nipple, while chest fat feels softer and is more evenly distributed. It often causes a distinct contour or puffiness that does not flatten with weight loss or exercise.
—
How to Determine if You Have Breast Enlargement?
The pinch test is a simple way to assess whether you might have gynecomastia at home:
- Lie on your back to allow the chest tissue to relax.
- Use your thumb and forefinger to gently pinch the tissue surrounding and directly under your nipple.
- Feel for a firm, rubbery disc or mound beneath the areola. Gynecomastia tissue feels denser than fat.
- Compare both sides. It’s common for one side to be larger or more pronounced.
If you feel a distinct, rubbery mass, you may have gynecomastia rather than simple fat accumulation. If the tissue feels soft and uniform, it’s likely just fat.
Even men with low body fat can develop gynecomastia. If you are lean but notice a pronounced mound or puffiness beneath the nipple, especially if it’s firm to the touch, this is a classic sign. The condition is not limited to those who are overweight.
—
Diagnosis and Next Steps
A definitive diagnosis involves a physical examination by an experienced plastic surgeon like Dr. Erella, who will assess the nature and distribution of the breast tissue. Sometimes, additional tests such as bloodwork or imaging may be used to rule out other causes.
If your self-exam suggests gynecomastia or you remain unsure, schedule a consultation with Dr. Erella at Aspira Plastic Surgery. Early evaluation can address your concerns and guide you to the most effective treatment.
—
Treatment Options
Conservative Treatments for Enlarged Breasts
In many cases of puberty-related gynecomastia, the condition resolves within months to a couple of years. For adults, persistent gynecomastia is unlikely to disappear without intervention.
While weight loss and chest exercises can reduce overall fat, they do not eliminate the glandular tissue that defines gynecomastia. Persistent puffiness or firmness beneath the nipple usually requires medical assessment.
Medical Interventions to Address Hormonal Imbalances
If gynecomastia is caused by medication or a health condition, addressing the underlying issue may help. However, established glandular tissue rarely disappears without surgical intervention.
Liposuction
Liposuction alone may be sufficient if the enlargement is caused by excess adipose tissue (fat deposits). However, true gynecomastia often requires removal of dense glandular tissue as well.
Surgical Removal of Excess Breast Tissue
Surgical male breast reduction removes the excess glandular tissue and, if necessary, excess fat and skin to restore a flatter, more masculine chest contour. Recovery is generally straightforward. Most patients return to normal activities within a few days, with full exercise resuming after several weeks. Swelling and minor bruising subside over a few weeks, and final results become evident within months.
Alternative Treatments
There is no scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of herbal or alternative remedies for true gynecomastia. Most cases that persist beyond adolescence or result in significant discomfort are treated surgically.
—
Boosting Confidence and Self-Esteem With Gynecomastia Surgery
Many men with gynecomastia struggle with body image and social confidence. Correcting gynecomastia can help restore self-assurance, enabling you to wear fitted shirts, enjoy the beach, or participate in sports without self-consciousness.
You don’t have to let gynecomastia limit your activities or self-image. Modern treatments offer safe, effective solutions tailored to your needs.
—
Schedule Your Consultation Appointment at Aspira Plastic Surgery
Aspira Plastic Surgery provides confidential, compassionate, and individualized care for men seeking solutions for gynecomastia. With extensive experience in male breast reduction, Dr. Erella offers proven results and a patient-centered approach. Discover more about Dr. Erella and the full range of procedures offered.
Why Is It Crucial to Choose a Board-Certified Plastic Surgeon?
Choosing a board-certified plastic surgeon like Dr. Erella is essential for safe and effective male breast reduction surgery. Board certification ensures the surgeon has completed rigorous training, adheres to high standards, and possesses specialized expertise in this procedure. This level of qualification helps deliver optimal outcomes with minimized risks and complications.
—
Conclusion
So, how to know if you have gynecomastia? The best way is to schedule a consultation with an experienced surgeon to take control of your health and confidence. If you notice firm tissue beneath your nipple, puffiness, or tenderness, consider a professional evaluation with Dr. Erella at Aspira Plastic Surgery. Proven treatments are available to help you achieve a flatter, more masculine chest and renewed self-assurance.